Infographic on Rice Irrigation
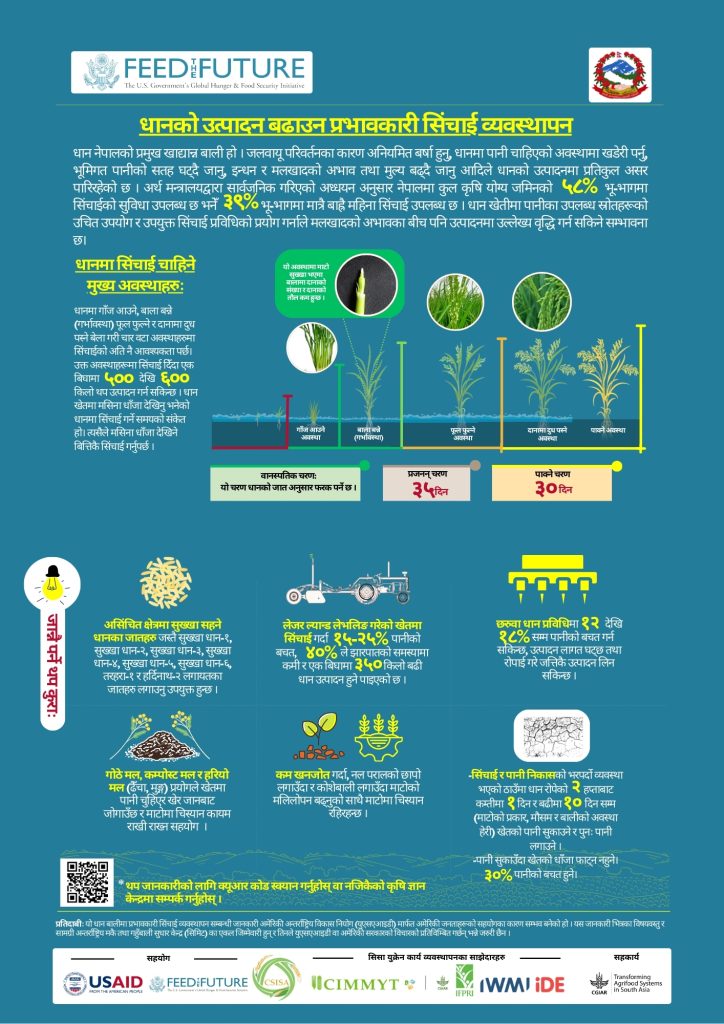
Rice is the primary staple crop in Nepal, but its production faces severe challenges due to climate change, erratic rainfall, drought, declining groundwater levels, fuel and fertilizer shortages, and rising prices. Climate change is causing more extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, which can damage crops and reduce yields. Unpredictable rainfall patterns can also make it difficult for farmers to plan their planting and irrigation schedules. Drought during critical growth stages can be particularly devastating, as it can lead to crop failure. This is a major concern in Nepal, where the monsoon rains are often erratic and unreliable. Declining groundwater levels are also a problem in many parts of Nepal. As groundwater levels fall, it becomes more difficult for farmers to irrigate their crops, which can lead to lower yields.
Fuel and fertilizer shortages can also make it difficult and expensive for farmers to produce rice. Fuel is needed to power irrigation pumps and machinery, while fertilizer is essential for crop growth. Rising prices are another challenge facing rice farmers in Nepal. The cost of inputs, such as fuel and fertilizer, has been increasing in recent years, which has put a strain on farmers’ budgets. Despite these challenges, there are ways to boost rice production in Nepal. One way is to improve irrigation facilities. According to a report by the Ministry of Finance, only 39% of Nepal’s arable land benefits from year-round irrigation. By improving irrigation systems, farmers can ensure that their crops have access to water during the dry season, which can help to reduce the risk of crop failure. Another way to boost rice production is to adopt suitable irrigation methods. For example, drip irrigation, precision agriculture, and integrated pest management can be used to conserve water and improve crop yields.
Finally, farmers can also improve rice production by using improved varieties of rice that are more resistant to pests and diseases. These varieties can help to reduce crop losses and improve yields. By taking these steps, it is possible to boost rice production and help ensure food security for the country’s population. The one-pager advisory focuses on using agricultural tools and techniques to improve rice yields.
Tags: CSISA Nepal, mechanization, Nepal, Surface Water Irrigation
