CSISA in Nepal
Cereal and pulse yields in Nepal fall well below the regional averages and present rates of increase won’t meet long-term domestic requirements. Factors that contribute to low staple crop performance in Nepal include scarce farm labor, poor knowledge of best agricultural management practices, lack of irrigation and mechanization and farmers’ inability to take risks and invest in new technologies. Also, innovative applied research has long been underfunded and research benefits have rarely reached farmers.
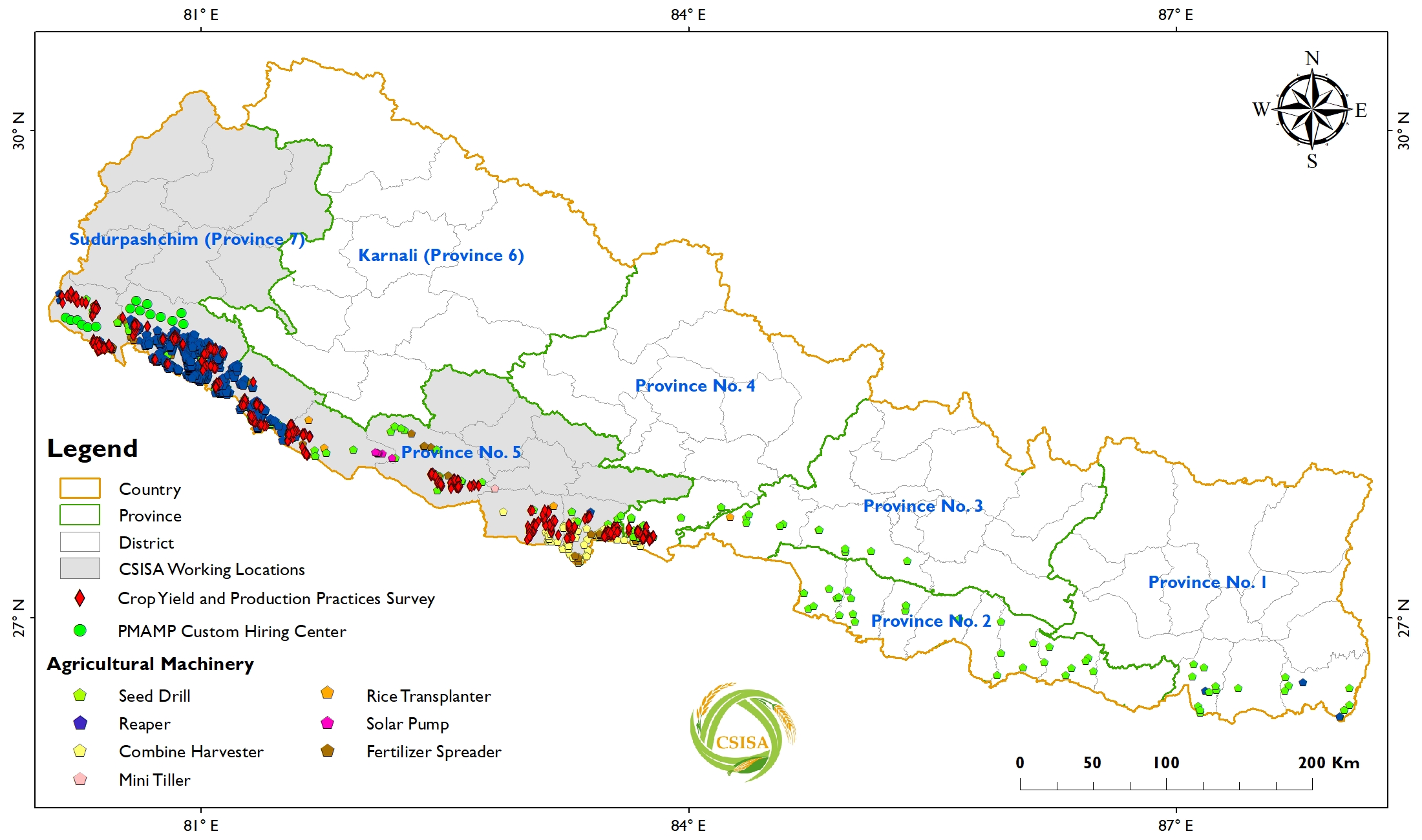
Nepal’s Mid and Far West development regions are most acutely affected by these constraints as these regions have the highest poverty and receive the lowest investment from the private sector. As a result, CSISA works in Nepal’s Terai plains and mid-hills, where the scope for improving farmers’ lives through agriculture is greatest.
The project works with partners who can help to rapidly and broadly increase the adoption of sustainable intensification technologies at scale. Its partners include Feed the Future’s KISAN project, government agencies, farmers’ groups, service providers, agro-dealers, seed enterprises and other private sector companies. The project’s interventions in Nepal include:
- The intensification and diversification of pulses (lentil and mung bean) and their adoption at scale
- Scaling up of cropping system-based approaches for sustainably intensifying wheat and minimizing terminal heat stress
- Facilitation of efficient and low-risk strategies for the precise and productive use of nutrients
- Establishing robust seed systems that ensure timely access to elite cultivars and hybrids
- Promoting scale-appropriate mechanization and irrigation
- Directly sown rice (DSR) to address labor and energy constraints to precision rice establishment
- Deployment of better-bet agronomic messaging through input dealer networks and development partners
- Income-generating maize production in neglected hill and plateau ecologies
- Integrated weed management to facilitate sustainable intensification transitions in rice
- Coping with climate extremes in rice-wheat cropping systems
CSISA COVID-19 response and resilience Activity – Infographic as of May 2024.
The CSISA-COVID response Activity began as an 18-month (from July ’20 to December’ 21) buy-in from the USAID/Nepal mission to the broader CSISA program. It aims to rapidly and effectively respond to the threats posed by the COVID-19 crisis that undermines the recovery and sustained resilience of farmers in the Feed the Future (FtF) Zone of Nepal, with two initial Objectives:
Objective I: Enable rapid, targeted, and effective agricultural COVID-19 crisis response through scale-appropriate farm mechanization and rural services provision
This objective pertains to the expanded use of scale-appropriate farm machinery to generate employment, lower production costs for farmers, and create new entrepreneurship opportunities in the context of a COVID-19-affected Nepal. Our main partner for this Objective is iDE/Nepal, who will be providing expertise on business models.
Key outcomes from Objective I include at least 4,500 individual farmers are anticipated to benefit as the key outputs are focused on expanding scale-appropriate land preparation, planting, irrigation, harvesting or post-harvest machinery services provided by service providers or custom hiring centers.
Objective II: Break the smallholder irrigation bottleneck and build rural resilience to the COVID-19 crisis
The second objective focuses on efforts to develop appropriate and sustainable irrigation planning and development in Nepal, while also considering how irrigation can increase resilience and generate income for smallholder farmers in COVID-19 crisis-affected districts of the FtF Zone. Our main partners for this Objective are IWMI, Texas A&M and Cornell University. They will provide support on predictive models and scenarios analysis to provide local, district and provincial level assessment of water resources.
Following the second wave of COVID-19 in 2021, additional funding was received for new and extended activities that will span from September 2021 through June 2023. The third objective aims to provide emergency short-term and medium-term recovery and relief in the agricultural sector following the second wave.
Objective III: Support rapid response and resilience-building from the second wave of COVID-19 in Nepal’s agri-food systems
The third objective aims to effectively rebuild key elements of Nepal’s agri-food systems and marginalized groups in the FtF zone that have been disproportionately affected by the second wave of the COVID-19 crisis. Key areas of intervention focus on the provision of access to finance for small- and medium-scale agricultural input and services provision businesses, recovery, and response in the post-harvest value chain, with emphasis on financial products to benefit businesses involved in perishable farm product marketing and distribution, and expansion of digital banking services supporting socially-distanced agricultural finance transactions. In addition, interventions focus on scaling out agricultural mechanization services through geographical expansion to new districts.
Earthquake Recovery Support Program (EQRSP)
The 2015 earthquake and subsequent aftershocks that struck Nepal had huge negative impacts on the country’s agriculture and food security. An estimated 8 million were affected by the earthquakes, with smallholders in hilly regions being the most hard-hit.
In response to the devastation, USAID-Nepal funded a support program from June 2015 to September 2016 that was implemented by CSISA in close coordination with the Ministry of Agricultural Development. The program distributed 50,000-grain storage bags, 30 cocoons for community grain storage, 400 mini-tillers and other modern agriculture power tools (e.g., reapers, maize shellers, seeders), 800 sets (5 items in a set) of small agricultural hand tools and 20,000 posters on better-bet agronomic practices for rice and maize.
The districts that received support included Dolkha, Kavre, Khotang, Makwanpur, Nuwakot, Ramechap, Sindhupalchowk, and Solukhumbu.
CSISA Agronomy and Seed Systems Scaling in Nepal
CSISA-Scaling ran from 2014-2019 and had a large-scale and durable impact on Nepal’s cereal-based agricultural food systems. The activity had a significant impact on wheat, maize, and pulse production systems in the Feed the Future zone. Among farmers adopting stress-tolerant varieties, improved seed, and implementing climate-smart and resilient farm management practices.
The activity’s main objectives were:
- Strengthening seed systems so farmers have timely access to improved, stress-tolerant varieties and hybrids for pulses, wheat and maize;
- Targeting geographic niches and identifying management practices that enable cropping system intensification through the inclusion of lentils and mung beans as new crops cultivable by resource-poor farmers;
- Recommending best management practices for wheat, including scale-appropriate mechanization technologies that help farmers plant early and avoid terminal heat while addressing rural labor bottlenecks;
- Facilitating market development for small-scale technologies that enable precise nutrient management; and
- Supporting the expansion of the private sector in the Feed the Future Zone of Influence in Nepal, including the availability of appropriate agricultural mechanization options, including spare parts, improved mechanic services, and expanding the number of machinery service providers to facilitate affordable access among farmers for mechanization technologies.
Key project achievements include:
- Large-scale impact in Nepal’s Feed the Future Zone: The CSISA Agronomy and Seed Scaling project has had a large-scale and durable impact on Nepal’s cereal-based agricultural food systems: 65,843 farmers have applied improved technologies and/or management practices as a result of project interventions on 30,811 hectares of cropland. Forty percent – 26,403 people – of farmers applying improved technologies and resilience-enhancing management practices were women.
- Expanding access to resilient crop management practices and stress-tolerant seed: The project had a significant impact on wheat, maize and pulse production systems in the Feed the Future Zone. Among farmers adopting stress-tolerant varieties, improved seed, and implementing climate-smart and resilient farm management practices, more than 45,223 were farmers growers who applied improved technologies in more than 21,175 ha of land. 10,576 maize farmers also applied improved technologies on 4,421 ha, while 8,003 farmers adopted mungbean as a new crop in Nepal and grew it on 2,122 ha of cropland. Another 3,910 farmers used climactically resilient production methods to grow lentils on 1,459 hectares.
- Private-sector-led development: The CSISA Agronomy and Seed Systems Scaling project supported numerous seed companies, agricultural input dealers, machinery manufacturers, importers and dealers, and machinery services providers to improve their business performance across the Feed the Future Zone.
- Strategic trainings leads to impact: To achieve the above, 2,013 lead farmers, government collaborators, civil society organization representatives and private sector staff received enhanced training on seed systems, resilient varieties, better-bet agronomic practices for cereals and pulses, and appropriate agricultural mechanization business models. 20% of those trained were women.
- Durable and long-lasting changes and improvements in farmer access resulted from this project: (a) improved, stress-tolerant varieties and hybrids for pulses, wheat and maize, (b) targeted and production of mung beans and pulses among resource-poor farmers, (c) climate-resilient enhancing and affordable wheat production technologies and practices, (d) viable options for more precise and efficient nutrient management, while (e) facilitating market development and value chains for scale-appropriate farm pieces of machinery that reduce labor-bottlenecks and assist women-headed households inefficient farm management.
For the CSISA-Scaling final report, click here.